Recently a client changed their OCS from public routed addresses for the Edge role to a NAT environment. This necessitated changing their firewall (ISA).
The online documentation for Office Communications Server 2007 R2 Firewall Requirements for External User Access makes the following statement:
Publicly Routable IP Address
In any location with multiple Edge Servers deployed behind a load balancer, the external firewall cannot function as a network address translation (NAT). However, in a site with only a single Edge Server deployed, the external firewall can be configured as a NAT.
If you do so, configure the NAT as a destination network address translation (DNAT) for inbound traffic—in other words, configure any firewall filter used for traffic from the Internet to the Edge Server with DNAT, and configure any firewall filter for traffic going from the Edge Server to the Internet (outbound traffic) as a source network address translation (SNAT). The inbound and outbound filters must map to the same public IP address and the same private IP address…
Then a little following that, the documentation make this statement in a note:
In addition to being supported as a reverse proxy, Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server is supported as a firewall for Office Communications Server 2007 R2. The following versions of ISA are supported as a firewall:
- ISA Server 2006
- ISA Server 2004
If you use ISA Server as your firewall, configuring it as a NAT is not supported because ISA Server 2006 does not support static NAT.
www.isaserver.org has an excellent tutorial on how to configure ISA 2006 to support OCS 2007, a second IP scope, and allow for an Office Communications Server 2007 R1/R2 Edge server to live in your DMZ.
But, based on the above quote and article, and assuming we have only one IP scope to work with, and we want to use NAT because we only have one Edge, what are TMG and ISA users to do? What follows is one method that works; please be aware that this was developed for a TMG (Threat Management Gateway) environment, and YMMV. However, I am also confident that it will work on ISA 2006 (tested in lab) also and allow R2 Edge to NAT when using TMG and ISA 2006 SP1.
What won’t work with ISA and this configuration is Federation. This is because ISA will not send the SIP packets OUT from the assigned Access Edge interface, but send the packets out from the primary ISA address. TMG gets around this by allowing you to choose the network relationship - effectively creating the 1:1 NAT that is needed.
For the routable addressing scheme as mentioned shown in the isaserver.org tutorial, the full monte of listeners and rules is used along with certificates that need to be exported, imported, and configured. This method is much easier, actually, and does not use listeners and certificates, just firewall access rules. Before you go much further, you should note that this solution may or may not meet your organization’s security needs. YMMV, Caveat Emptor, etc.
For this demonstration, the ISA external interface is a 10.x.x.x/24 network. The internal interface is connected to a 1.x.x.x/24 network. Note that we have sufficient addresses to give each OCS Edge role its’ own address; we won’t be doing the port change routine. Further note that if you do that, this will still work, just change the ports on the firewall rules. The OCS Edge server has already been told that the A/V role is behind a NAT, so that part of the system is all ready to go. Let’s take a quick look at our IP usage for this scenario and how that corresponds to our internal OCS deployment.
Internal:
Access Edge: 1.1.1.37
Web Conferencing: 1.1.1.39
A/V: 1.1.1.38
External:
Access Edge (SIP): 10.10.10.37
Web Conferencing (LM): 10.10.10.39
A/V (AV): 10.10.10.38
Graphically, this is our IP flow for both in and out, and for OCS, we need to maintain that in/out relationship:
Let’s put together the objects and rules we need on the TMG/ISA to allow OCS R2 to NAT. First, we need to create some user-defined protocols to use with our OCS rules. Here are the protocols that I created to support OCS Edge Roles:
To create these user-defined protocols, access the toolbox, select protocols, then “user-defined” and choose New from the dropdown:
Fill in the name of the first protocol and select “Next”
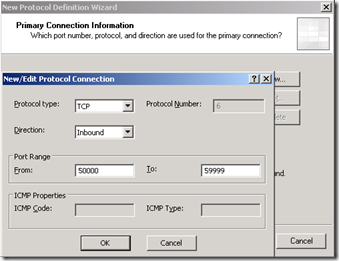
On the next page, select “New” and then complete the protocol information as shown:
Click on OK, Next, Next again, and then Finish to complete the first user-defined protocol. In your toolbox, under user-defined protocols, you should see your new protocol. Double-click it and verify that the protocol definition looks like our example here.
Now create the remaining two user-defined protocols using this information:
| Protocol name | AV TCP In |
| Protocol type | TCP |
| Direction | Inbound |
| Port Range | 50000-59999 |
| Protocol name | Sip-In |
| Protocol type | TCP |
| Direction | Inbound |
| Port Range | 5061 |
| Protocol name | AV UDP in |
| Protocol type | UDP |
| Direction | Receive/Send |
| Port Range | 3478, 50000-59999 |
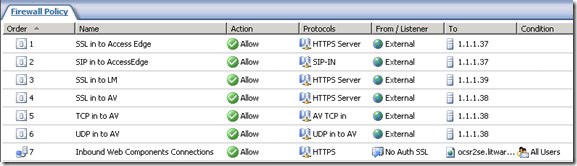
With the protocols done, we can now create the access rules. Here are the rules we need:
Rule #7 is for the OCS Reverse Proxy to the Web Components. We will not be changing that rule in any way.
Rules 1-6 all are constructed in the same manner. These are actually created with the “Publish Non-Web Server Protocols” wizard. After looking at the first rule, I will present the remainder in table form.
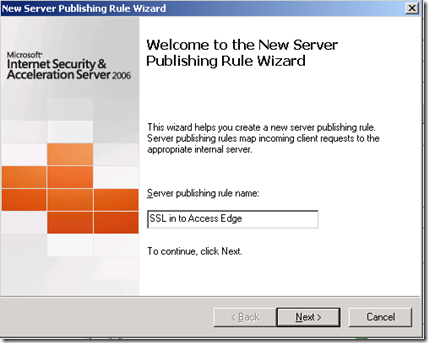
Start by selecting the new task wizard:
Give your new rule a name:
Enter in the IP address of the appropriate Edge role external interface. In our case, 1.1.1.37 is the Access Edge external interface.
Choose the appropriate protocol for this rule. This is an SSL rule, so HTTPS Server is selected.
Select the Network Listener IP Addresses. For this example, “External”
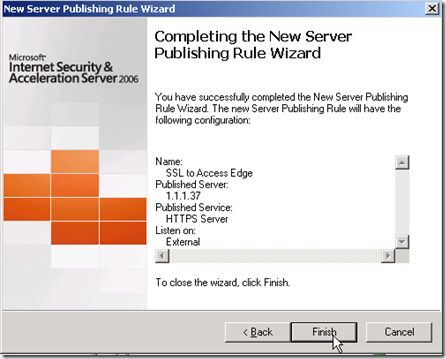
Click on Address and select your specific External address for this service. In this example, 10.10.10.37.
Click on finish and we are done with the first rule.
Now, create the remaining rules using the “Publish Non-Web Server Protocols” task wizard and the following information.
| Rule Name | SSL in to Access Edge |
| Select Server | IP Address for outside edge of OCS Access Edge Role |
| Selected Protocol | HTTPS Server |
| Network Listener IP Addresses | External, and modify to specific External IP for Access Edge |
| Rule Name | SIP in to Access Edge |
| Select Server | IP Address for outside edge of OCS Access Edge Role |
| Selected Protocol | SIP-In |
| Network Listener IP Addresses | External, and modify to specific External IP for Access Edge |
| Rule Name | SSL in to LM |
| Select Server | IP Address for outside edge of OCS Web Conferencing Edge Role |
| Selected Protocol | HTTPS Server |
| Network Listener IP Addresses | External, and modify to specific External IP for Web Conferencing Edge |
| Rule Name | SSL in to AV |
| Select Server | IP Address for outside edge of OCS AV Edge Role |
| Selected Protocol | HTTPS Server |
| Network Listener IP Addresses | External, and modify to specific External IP for AV Edge |
| Rule Name | TCP in to AV |
| Select Server | IP Address for outside edge of OCS AV Edge Role |
| Selected Protocol | AV TCP in |
| Network Listener IP Addresses | External, and modify to specific External IP for AV Edge |
| Rule Name | UDP in to AV |
| Select Server | IP Address for outside edge of OCS AV Edge Role |
| Selected Protocol | AV UDP in |
| Network Listener IP Addresses | External, and modify to specific External IP for AV Edge |
Remember to apply all your changes! We have now configured our TMG/ISA to allow for full edge traffic across a single NAT’d public IP subnet. We did not discuss the Reverse Proxy rule for the Web Components, nor did we affect any changes to the base documentation for that service. Make sure that your Edge Server can resolve the EXTERNAL IP of the AV edge service. In this example, this would be 10.10.10.38. I use a host file for this.
I hope that this has been helpful in getting you going with a NAT’d TMG/ISA and OCS 2007 R2 environment.